With more threat actors targeting companies than ever before, businesses need to handle their data storage devices more responsibly and carefully. Doing so will reduce and mitigate the risks of a data breach that could ruin their reputation and result in massive losses.
However, that does not mean that companies can destroy their computers as they see fit. Organizations that fail to dispose of obsolete data in the right way will expose themselves to data leaks, blackmail, and other security issues.
Here are the top seven data destruction myths that companies believe in—but shouldn’t be.
1. Deleting or Moving Something to the Trash Is Good Enough
One of the most popular data destruction myths is that you can wipe data by simply deleting it or moving it to the trash.
In reality, deleting or moving something to the trash just removes pointers that tell the device where the data is. Think of it this way: removing a road sign doesn’t remove the road. Deleting a file is just removing the sign, but the road is still accessible. Computers use a lot of temporary, hidden memory, which means that the data and files will still exist as “fingerprints” in various parts of your device even after deleting or moving them.
In other words, the data is still on the drive — it is just harder to find. Computer specialists, including threat actors, can easily use tools to recover this “deleted” data.
2. Formatting a Hard Drive Erases Your Data
Another common data destruction myth is that formatting a hard drive — that is, wiping the disk back to an empty state — makes data untraceable.
Formatting a hard drive does not permanently wipe its contents. It just erases the address tables, making it much harder to recover the files. Using the example of roads, this would be like shredding your map – but the roads are still there. Threat actors can easily access the deleted information with file recovery software. A formatted drive can be understood as being rewritten or written over with new data, but that’s not really starting with a clean slate as if you have a brand new fresh drive, and it doesn’t “scramble” the old data the way you might imagine it does.
3. Factory Resets Reset Your Device and Data
Similarly, many organizations believe that factory resets erase all of their data. While returning a computer to its factory settings makes it look like you have deleted all of your data, in reality, there is no way to guarantee that all of the old data is removed, until you overwrite it with new data. A factory reset re-establishes the conditions that the device was sold in, but it doesn’t actually rewind time.
4. Degaussing Magnets Wipe Data Off Hard Drives
Since data is stored magnetically on hard drives, it seems reasonable to assume that you can use degaussing magnets to wipe the data. Degaussing magnets produce powerful magnetic fields that can physically destroy data. However, not all hard drives are susceptible to magnetic damage, especially the more modern ones.
There are two kinds of drives: hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SDDs). HDDs can potentially be damaged by magnets since they generate binary code by changing the charge of magnetic bits in the drive. However, these magnets would have to be stronger than most Tesla or MRI magnets. Magnets also don’t delete or overwrite data, they just damage it, making it harder – but not impossible – to access and restore.
As for SDDs, they maintain binary code in a stored charge, and contain no magnets themselves. Exposing them to a magnet will not result in damage to the data the way it can with an HDD.
5. Threat Actors Do Not Target Small Businesses
Many organizations believe that they do not need certified data destruction services because threat actors only target leading-edge companies like Microsoft or Apple.
In reality, 43% of all U.S. corporate data breaches in 2021 involved small businesses. This means that companies of all sizes need certified data destruction services to protect themselves and their clients.
6. Data Destruction Services Are Too Expensive
Some small companies believe that securely managing their data is beyond their budget. Although reliable data destruction services are paid solutions, the cost of partnering with a data destruction company pales compared to the risks of handling everything on your own.
Without a dedicated data destruction partner, you are likely to face the following consequences:
- Data breaches that hurt your reputation, lower your revenue, and put your clients and employees in danger of crimes such as identity theft and extortion
- Huge fines for failing to comply with privacy regulations like the European Union (EU)’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
7. Drilling Holes or Smashing Computers Makes Data Untraceable
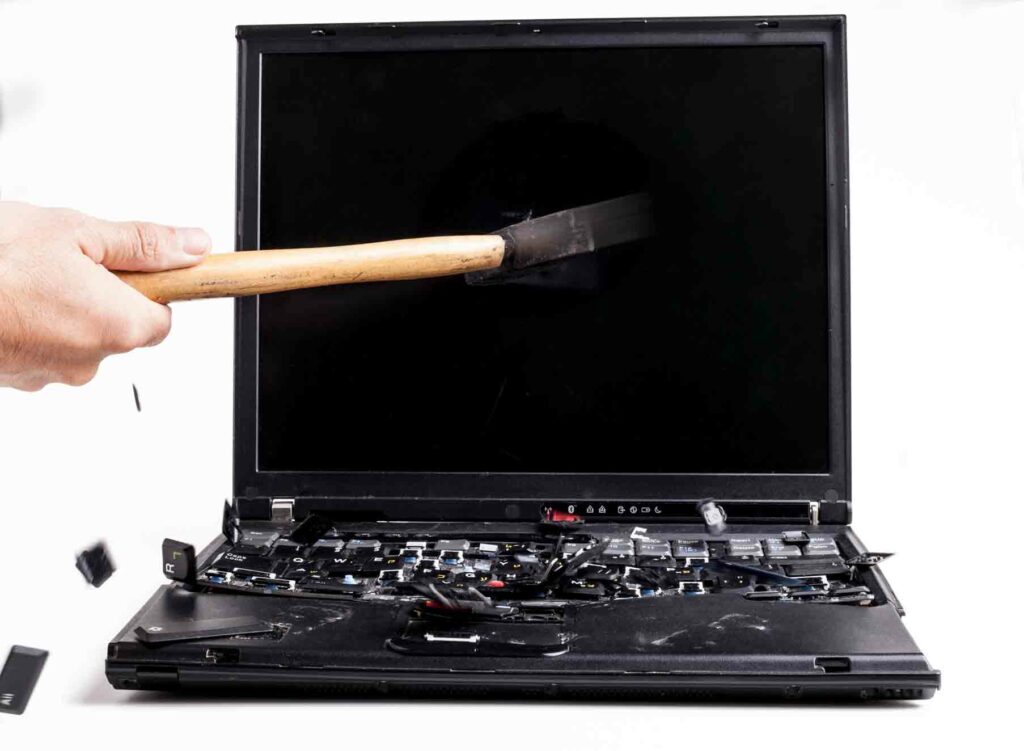

Finally, many companies believe that drilling, smashing, or otherwise physically dismantling hard drives and computers is a sure-fire way to destroy data. Physical destruction is a legitimate way to remove data, but the do-it-yourself method leaves holes in your security.
Whether you use a drill, a hammer, a chainsaw or run over it with your car, information can still be recovered from a hard drive as long as parts of the hard drive remain intact. You and your clients’ data remain at risk as long as a single solid-state data chip survives the destruction process.
Additionally, physically damaging computers can release dangerous chemicals into the environment. These chemicals are safe while the computer is in use and provide benefits like fireproofing, but can have harmful effects if inhaled or ingested. This destruction process is also incredibly inefficient since you need to spend many hours checking to see if every part has been adequately drilled or smashed. Even if you think you have adequately destroyed everything, there is no real way of knowing whether you and your clients are safe from potential security threats.
This is where certified data destruction services come in. Cobalt, for instance, has a secure and environmentally-friendly system for destroying electronics that meets the highest possible standards and gives you peace of mind.
Specifically, Cobalt offers:
- Bulk electronics disposal: Take care of your entire inventory of retired devices at once, safely and conveniently, and receive a certificate of proof of disposal.
- ITAD management: Add an ongoing electronics recycling program as part of your IT lifecycle, supported by documentation and reports.
- Mobile hard drive shredding: Cobalt comes to you and shreds hard drives right in front of you – not a byte leaves your sight.
- Secure transportation for electronics: A Cobalt team can come prepare, package, load and ship your inventory of electronics to our secure facility in Middletown, Ohio.
Electronics recycling events: Cobalt can help you host a collection event for your employees, clients, or community.
Choose Cobalt for Certified Physical Destruction of Data
Some of these secure destruction of data methods may be acceptable to an individual. However, if you run a business with a lot of devices to dispose of and a lot of sensitive data that could be used against you and your clients, you should take extra steps to protect yourself from liability.
That is why you should partner with a certified IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) company. The right ITAD company won’t just take your electronics off your hands, they will:
- Comply with all relevant privacy laws and regulations
- Ensure that your data has been destroyed on every device
- Recycle and refurbish electronic assets if possible and as needed
- Use the right tools and methods to wipe your data
Protecting your data is a critical piece of retiring your technology assets responsibly. Now that you know these 7 data destruction myths, we hope you feel more confident in the data destruction process and are able to make an informed decision about how best to retire your old tech. If you have any other questions or want more information on Cobalt’s data destruction services, please don’t hesitate to reach out. We would be happy to help!